Step-by-step instructions for using open-source data for protecting brand and intellectual property.
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) can be used in different scenarios to support various intelligence collection needs. From supporting military operations to investigative journalism to discovering crimes and human rights abuses and reaching to academic research and business development. OSINT has proved to provide a cost-effective and efficient mean of intelligence gathering, including for corporate entities.
As the world moves steadily to become fully digital, enterprises worldwide face a growing digital challenge. The risk of counterfeiting in cyberspace has become a pressing issue worldwide. It costs enterprises billions of dollars of losses each year in revenue in addition to its social impact through losing thousands of jobs annually because of counterfeited products and goods. The US Chamber of Commerce estimates counterfeit goods cost the global economy over $500 billion annually. The Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress estimates that counterfeiting and piracy costs US companies more than $200 billion annually and leads to the loss of more than 750,000 jobs.
In this article, I will discuss how we can leverage OSINT in brand protection strategy; I will mention different tools and online services that can aid investigators in discovering counterfeit online activities and identifying who is behind them.
How to use OSINT for brand protection
There are various techniques to discover and track counterfeited goods and products. I will begin discussing counterfeited digital products, such as software programs, books, music, films and any copyrighted digital product.
Monitoring pirated websites
A pirated website is an online portal specialized in distributing counterfeited digital products. There are different types of online portals and internet messaging applications dedicated to distributing counterfeit digital products, such as:
Torrent websites are the primary medium used to distribute such content. Here is a list of top torrent websites to begin your search:
- Torrentz.eu
- Xtorx – Search different torrent websites
- Veoble – A Google custom search engine for searching different torrent websites
- Torrent Search – Search dozens of torrent websites
You can also use Google Dorks to find content on torrent websites; here is a search operator: filetype:torrent torrent
File-sharing websites may host such content, although their usage policy may not allow this, however, it is too difficult to monitor all files uploaded to these servers. Here are some websites to begin your search:
Some FTP servers host pirated content. Some web servers could leave their directories open to public access while hosting such pirated content. I found many universities hosting pirated software programs on unprotected web directories. Google does not index such content; however, we can still utilize some custom search operators to find them. Here are some examples:
- intitle:"index of" "parent directory" Adobe -rar OR zip
- intitle:"index of" "parent directory" celine dion -mp3 OR m4a
- Movie or song Name -inurl:(htm|html|php|pls|txt) intitle:index.of "last modified" (mp4|wma|aac|avi|mp3) - Change the Movie or song Name with the once you want to download.
- intitle:"index of" inurl:ftp office site:edu (see Figure 1)
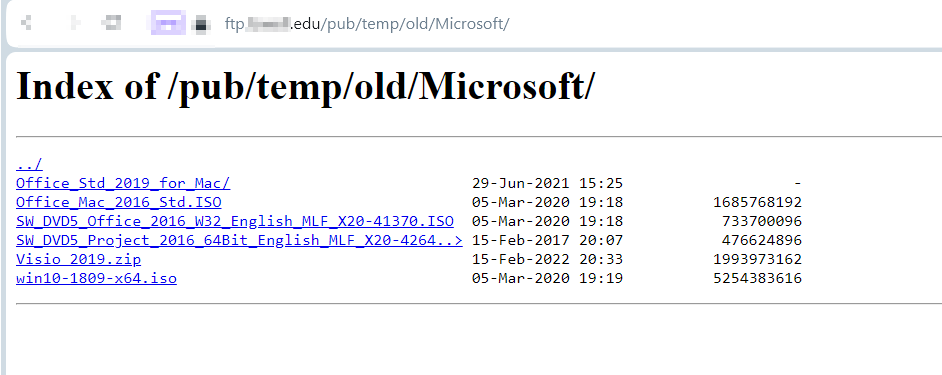
Figure 1 - Some unprotected FTP servers could host cracked versions of software products
Internet messaging applications such as Telegram (see Figure 2) become a new vehicle for distributing pirated digital products. Performing OSINT on Telegram needs a dedicated article. However, for this article, I will provide links to dedicated search engines and Telegram directories to begin searching and discovering Telegram channels quickly.
- Teleteg
- Lyzem
- Telegramic Channels Directory
- Telegago – a custom Google search engine for searching within the Telegram network
- Telegram Channels
- Search Telegram Groups– Search Telegram group links
- We can also use Google Dorks to find Telegram channels using the following query: site:telemetr.me
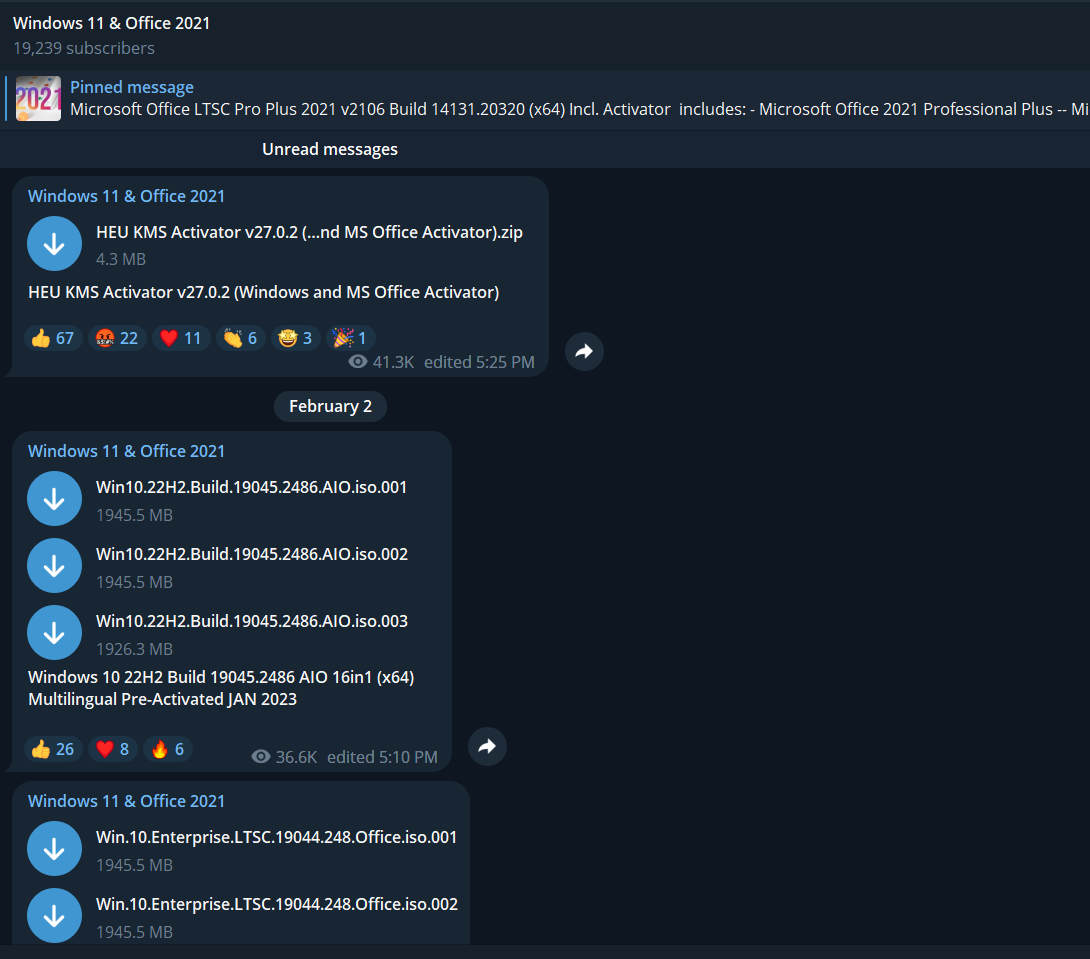
Figure 2 - A Telegram channel used for hosting and distributing cracked software programs
Reverse image search
For physical product types, such as watches, clothes, cosmetics and electronic devices, we can initiate our search using reverse image search to identify counterfeits. There are many websites for conducting reverse image searches, the most popular ones are:
- Reverse Image Search – Search Bing, Google and Yahoo!
- Tineye
- Yandex
For example, due to consumer demands, sports footwear is the most popular counterfeit product. To discover where counterfeit shoes are promoted, we can take the original image of the shoes (e.g., from Nike or Adidas official stores) and conduct a reverse image search to find all websites selling the same item. Counterfeited products will generally sell at a lower price and at online stores that are primarily based in China, Turkey, UAE and countries in Southeast Asia.
Before describing how to investigate who is behind counterfeited websites, it is worth noting that the Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) each year releases a Review of Notorious Markets for Counterfeiting and Piracy. You can get the latest report here.
Investigating the ownership of the counterfeited website
After identifying the online merchant selling the counterfeited products, we can begin inspecting it to identify the following:
- Owner name/s
- Where the website is hosted (hosting company)
- Is there a physical location for this merchant, or is it only based online?
- Where is the company behind the website registered?
- What payment methods it use to receive customers' payments online?
- What are customer reviews?
- Does it have a presence on social media? And what are the number of followers of their social media pages?
The first thing we need to begin with is investigating the domain name. This allows us to discover the company owner, other linked domain names, hosting provider, domain register and the date when this domain name was first registered, among other important information.
Domain name Whois information
There are different services to reveal domain name Whois information. However, it is worth noting that some domain name owners may remove their Whois information from the database.
The Whois information of a domain name could reveal some information that can lead to other places. If we are not lucky to find different trails, then we can check the website's previous history.
Identifying the hosting company
Identifying the hosting company can be beneficial to file a complaint against the website selling counterfeit products so we can stop it online. Here are two services for identifying the hosting company of any domain name:
Usually, websites hosted outside the USA and EU countries could be more suspicious, and raising a counterfeit complaint against them is challenging.
Website history
Wayback Machine is the most popular online service for fetching previous screen captures of websites. A previous screen capture of a website could reveal the true owner's name, contact information (such as email and phone number) and other information that can lead to collecting vital information to support our ligation. This tool is integrated in Silo for Research. See Figure 3 for a previous screen capture of authentic8.com taken in 2003 showing their global distribution networks.
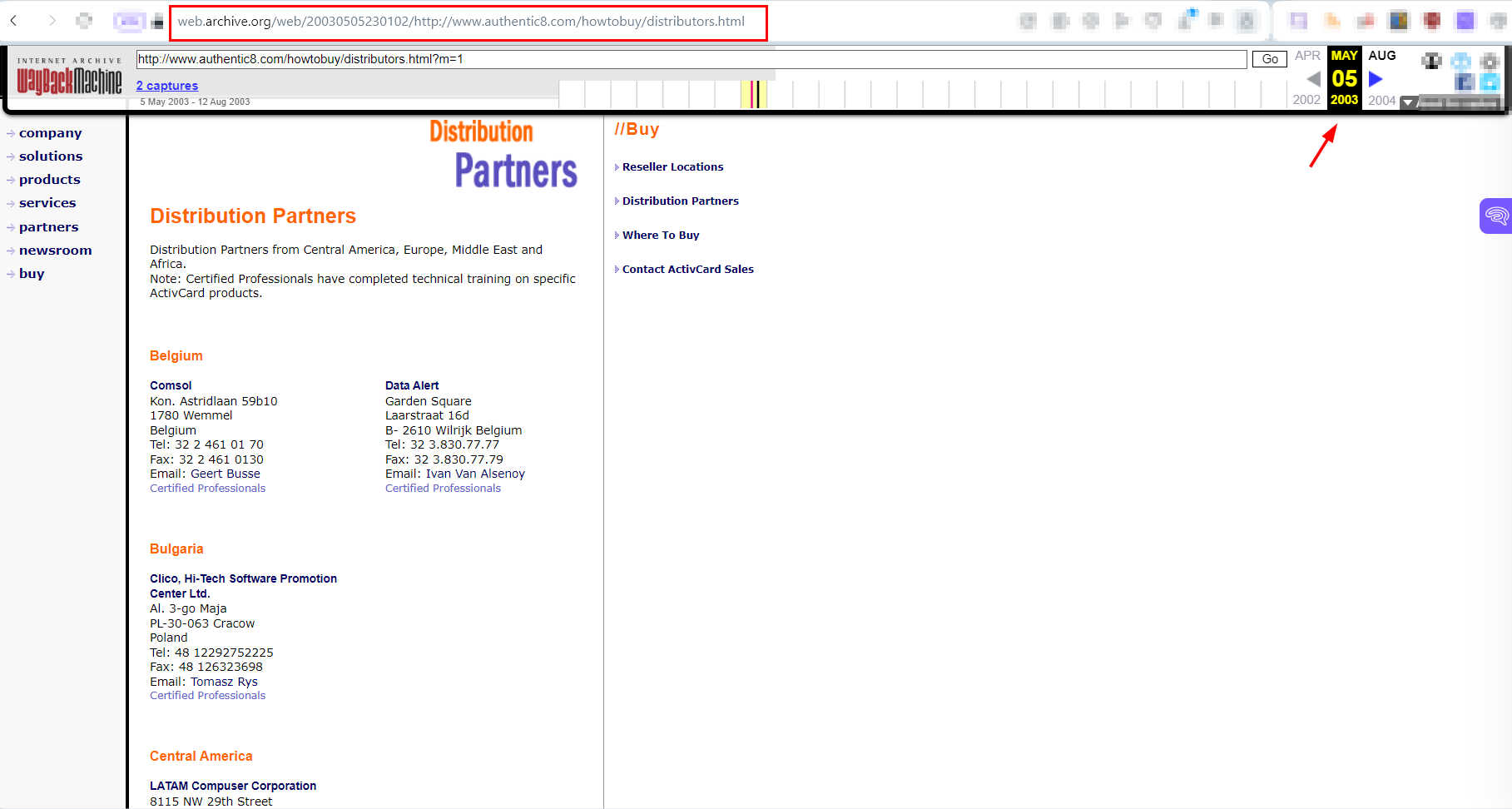
Figure 3 - Wayback Machine is helpful to get previous screen captures of websites
Technologies used to build the website
By inspecting the technical side of the counterfeited website, we may discover more information about it, such as linked domain names. Two popular websites for getting technical information about any website are:
For example, if we discover that the target website is using Google AdSense, we can extract the AdSense ID and conduct a reverse search to find all websites using the same ID. Here are two websites to conduct reverse Google AdSense or Google Analytics search (see Figure 4):
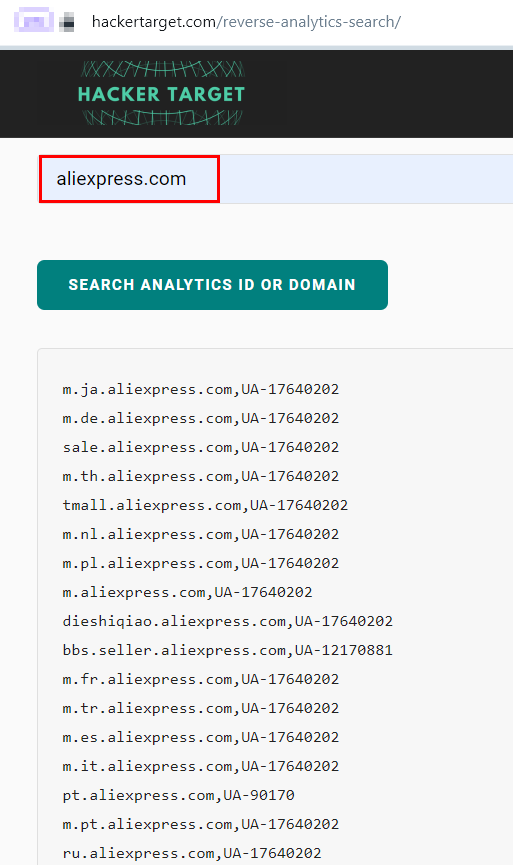
Figure 4 - Reverse Google Analytics is useful for finding all connected domain names
Connected domain names
If the target website does not use Google Analytics or AdSense services, we can use another method to find linked domain names. Whoxy is a free service for finding Whois information of domain names in addition to linked domain names. I checked TechCrunch.com to see linked domain names (see Figure 5).
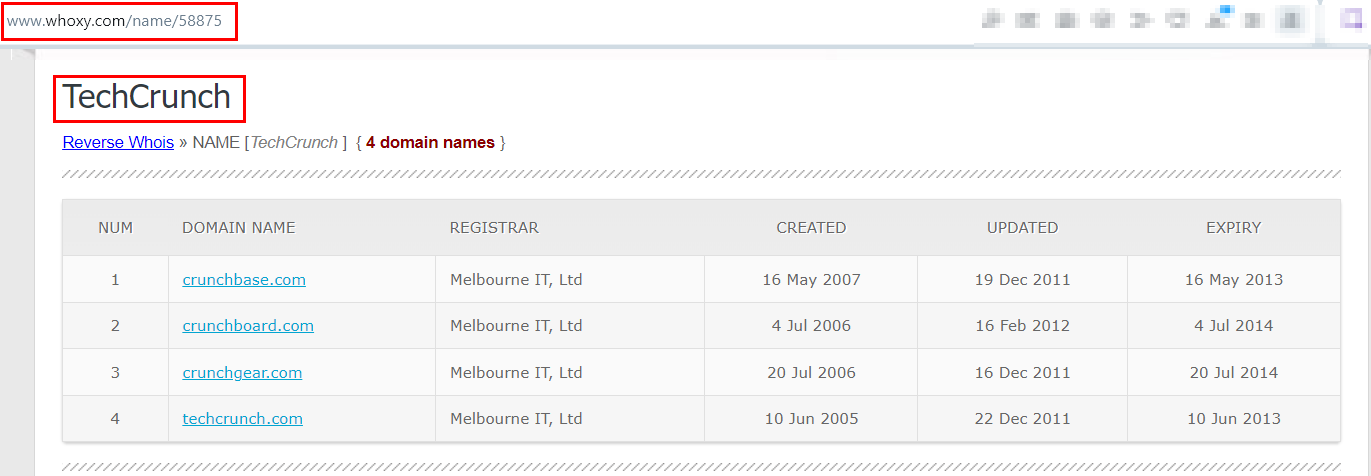
Figure 5 - Finding linked domain names to a particular domain name using whoxy.com
Searching corporates records
After getting enough information about the target company and its owners/business partners, we can search for its official corporate records. Here are some websites to start your search:
- Annual reports – Contains information for 10,146 international companies.
- CHINA COMPANY SEARCH ENGINE – Contains a comprehensive list of all Chines corporations registered in mainland China. You need to enter the Chinese company name in the Chines language not Latin characters.
- Annual reports of listed companies in Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange
- National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System – China official nationwide company registration search website. The website has a Chinese interface, so you should use a translation service like Google Translate.
- Zoominfo – Contains more than 100 million companies' profiles. You can search for a company using different criteria other than its name, such as email address, phone number or mailing address.
- European e-Justice Portal - Business registers of all EU countries, Iceland, Lichtenstein and Norway.
- UK Companies House – Find information about any UK company.
- Russian The Public Corporate Register (EGRUL) – Contains information about Russian companies.
Patent search
Many counterfeited products steal other individuals' or companies' patents to produce similar products without a license from the genuine inventor (or holder of the patent rights). Suppose we suspect that a modern invented product or design is stolen. In that case, we can conduct a patent search using the following resources grouped according to their country of origin.
- The Patent Public Search – USA
- Global Dossier – Worldwide
- European Patent Office (EPO) – EU patent database
- Japan Patent Office
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- Korean Intellectual Property Rights Information Service (KIPRIS)
- China National Intellectual Property Administration
- CIPO's Canadian Patent Database
- Taiwan patent database
For a full list of patent offices worldwide, please check this link.
Describing all methods and techniques to fight counterfeit goods and services cannot fit in one article. For instance, we still need to investigate transportation routes and track brand mentions on social media platforms and the darknet, which requires many articles to cover.
In this article, we shed light on counterfeit products' growing risk and discussed how we can leverage OSINT techniques to fight this risk. But using OSINT comes with other risks, including retribution for cutting off a lucrative counterfeit revenue stream. Make sure you are being safe and anonymous while conducting OSINT research. To learn more about why managed attribution offers superior protection to costly and gapping virtual machine and VPN setups, read more or request a demo.
Tags Anonymous research OSINT research

